- What Are Smart Contracts - Smart Contracts Explained
- How do Smart Contracts work?
- What Smart Contracts Promise To Do a.k.a Benefits of Smart Contracts
- 1. Autonomy
- 2. Accuracy
- 3. Transparency
- 4. High speed
- 5. Data storage
- 6. Trustability
- 7. Cost Savings
- 8. Robust Backup
- Applications of Smart Contracts in Different Industries and Sectors
- 1. Financial services
- 2. Healthcare
- 3. Media
- 4. Voting and Public Sector
- 5. Supply chain
- What Smart Contracts Does Not Promise To Do
- 1. Ease of Correction
- 2. Cases of Loophole
- 3.Third Party Elimination
- 4. Legal Unclarity
- 5. Management of Vague Terms & Conditions
- How to Overcome the Limitations of Smart Contract
There’s no denying the fact that Blockchain has changed the whole economy. The technology, with its characteristics of immutability, transparency, anonymity, decentralization, and security, has made myriad changes in the business processes.
But, one characteristic that has made blockchain even more popular is elimination of third-party intermediaries. The technology, in the form of smart contracts (especially ethereum smart contracts), lowers the chances of any process conflict, saves time, and makes the process cheaper, faster and efficient.
But, what exactly are Smart contracts? What makes them more popular than other blockchain applications?
Let’s find out together in this guide – starting with a simpler definition to smart contracts.
In a hurry? Jump directly to –
What Are Smart Contracts – Smart Contracts Explained
What Smart Contracts Promise To Do a.k.a Benefits of Smart Contracts
Applications of Smart Contracts in Different Industries and Sectors
What Smart Contracts Does Not Promise To Do
How to Overcome the Limitations of Smart Contract
What Are Smart Contracts – Smart Contracts Explained
Smart Contracts, as highlighted in our Entrepreneur’s Guide to Blockchain, is one of the three pillars of the Blockchain technology.
Smart Contracts help you exchange anything of value in a transparent, conflict-free ecosystem that is based on Blockchain.

Smart Contracts are basically self-executing contracts which are programmed in a way to ensure that the terms of agreements are met/unmet and then take a resulting action.
Talking of Smart Contracts, Know Which Platform – EOS or Ethereum is Winning the Race of Being the Best Smart Contract platform.
Now that you are up to speed with what Smart Contracts mean with our Smart Contracts Explained section, let us talk about what we lured you in for – The Smart Contract Benefits/ Offerings and the Smart Contract Limitations.
With the smart contracts definition cleared, let’s dive deeper and understand the working of this blockchain concept.
How do Smart Contracts work?
To understand how smart contracts in the blockchain environment work, let’s take an example.

Suppose there’s a person ‘Albert’ who wishes to sell his car to ‘Nancy’ in return of payment in cash. They form an agreement on the Ethereum blockchain via a smart contract, which states –
“WHEN Nancy pays $25,000 to Albert, THEN she will receive ownership of the car”.
Since this smart contract agreement is placed in a blockchain environment, it cannot be changed. Implying, Nancy need not fear that Albert will suddenly demand more money. Also, she need not pay an additional fee to third-party companies like banks, a lawyer or a car broker to prove that she has made the payment.
This implies, she won’t have to pay an extra commission or face delays in processing of the agreement due to any external factor. The smart contracts are executed automatically when the related condition is met.
Now as the working of smart contracts is explained, let us talk about what we lured you in for – The Smart Contract Benefits/ Offerings and the Smart Contract Limitations.
What Smart Contracts Promise To Do a.k.a Benefits of Smart Contracts
1. Autonomy
The foremost benefit of blockchain underlying smart contracts is that they are decentralized in nature. They do not require the involvement of any third party in the process. Meaning, the autonomy is maintained.
2. Accuracy
Smart Contracts are based on the requirement that all the terms and conditions are recorded explicitly.
3. Transparency
One of the prime benefits of smart contracts is that it minimizes the dispute cases to zero.
The TnCs of Smart Contract are visible and are accessible to all the parties, which negates the scope of the dispute. Also, since a smart contract is definite and comes with no between the line clauses, the chance of dispute gets eliminated.
4. High speed
As these contracts run on software codes, the speed of executing transactions are much quicker with Smart Contract as compared to real-world contracts, which calls for man-hours for documentation.
5. Data storage
Smart Contracts record a set of essential details in every transaction, meaning that your details that are recorded in the contract get stored for future records, permanently.
6. Trustability
Again, Smart Contracts come embossed with a myriad of features like – Transparency, Security, and Autonomy, without zero possibilities of bias, manipulation, and error. This adds trust to the ecosystem.
7. Cost Savings
By automating a majority of tasks and eliminating third-party intermediaries, smart contracts also lower down the cost associated with its implementation.
8. Robust Backup
Since smart contracts replicate all transactions, it becomes easier for parties to have a backup of all the transactions even when the data storage device fails.
With this covered, let us move to the next part of this smart contract guide, i.e, the use case of smart contracts.
You may like reading: Asset Tokenization on the Blockchain {A Complete Guide}
Applications of Smart Contracts in Different Industries and Sectors

1. Financial services
When talking about the implementation of smart contracts in financial industry, it helps in transforming the traditional services in numerous ways –
- Trade clearing – Lets you manage the approval workflow between the counterparties and transfer funds once the trade settlement amounts are calculated.
- Insurance Claim – Performs routing, error checking, and the approval workflow, once found correct, it transfers payment to the user once the payout is calculated on the basis of claim type and the underlying policy.
- Micro-insurance – Estimates and Transfers the micropayments on the basis of usage data collected from IoT enabled devices.
- Transparent auditing – Incorporates crucial tools for bookkeeping, eliminates the capability of infiltration of accounting records, and lets stakeholders participate in decision making in a transparent manner.
- Micro-lending – Empowers you to audit the value of the fundamental collateral and securely store them in a database, such that each transaction is quick, invariable, and transparent.
2. Healthcare
Smart contracts are also changing the healthcare landscape in the form of different uses, a few of which are –
- EMR – Enable transfer or access to the health record once the multi-signature approval is established between the providers and patients.
- Medical Research – Researchers can gain access to the users’ health data by making micropayments to the patients for their participation.
- Track Health – Track health-related events through the various IoT devices that the patients’ use and rewards can be generated when they hit a milestone.
- Health Insurance – Reduces inefficiencies in the current system by automatically adding patient details in policy forms and eliminating third-party intermediaries, along with preventing hack of the database.
3. Media
Blockchain-powered smart contracts come loaded with different properties that make it possible for anyone to relish the following benefits –
- Freedom to license a media the way a copyright owner wants to.
- Automated transactional tasks that were performed manually earlier.
- Faster, accurate, and cost-efficient processing
4. Voting and Public Sector
Public data can be stored on Blockchain and with the help of Smart Contract, the information can be sent to the parties asking for them, keeping the data owner in the loop.
Likewise, the voter criteria can be validated and specific actions can be taken by entering into the blockchain ecosystem.
5. Supply chain
The advent of smart contracts in the supply chain is also making it possible to perform various actions, such as –
- Payment transfer – It lets people transfer the payment once the multi-signature approval for the letter of credit is received.
- Product Provenance – It is used to issue port payments after custody change for the bills of lading is made. Also, it enables chain-of-custody for the products in the supply chain in which the party in custody can log evidence about the product.
What’s more, different types of smart contracts are revamping the IoT ecosystem. They, as a part of the Blockchain of Things system, are helping sensors and connected devices create their own nodes in the blockchain database, track orders in real-time, and this way, ensure the correctness of the product from the initial shipment to delivery end.
With such benefits and use cases, Smart contracts are becoming the face of various business verticals. It is encouraging various startups and established organizations to hire a reputed blockchain development company and become a part of the future of smart contracts. The one who’s market size is anticipated to be worth nearly USD 300 Mn by the year 2023.
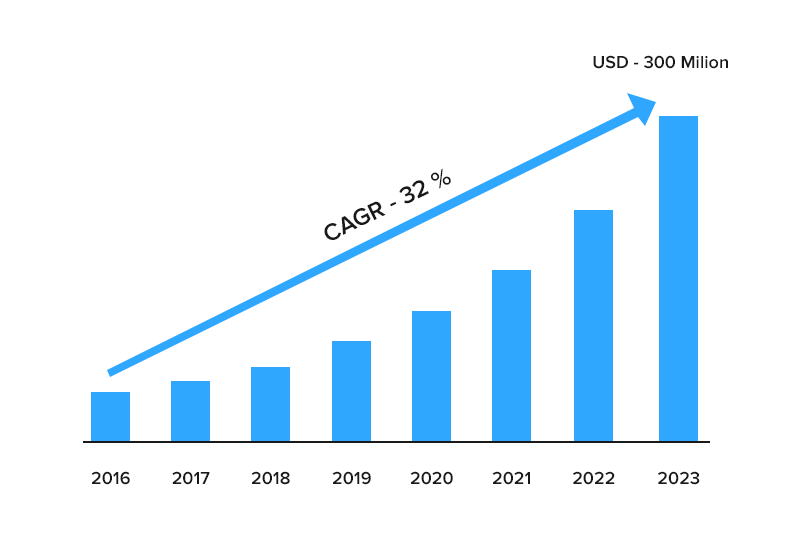
However, there’s a glitch.
Though loaded with a vast number of pros, Smart contracts in the blockchain environment are not fully-developed. They too have some limitations.
So, considering the same, let’s hit on the area which throws a light on the limitations of the Smart contract concept – one which are rarely talked about.
What Smart Contracts Does Not Promise To Do
1. Ease of Correction
Being a Blockchain element, Smart Contracts come with the same benefit of Immutability as Blockchain. While this immutability set standards in terms of security, there are a few limitations that come tagged along as well.
Since they are nearly impossible to change, even the slightest error in code can turn out to be expensive and time-consuming to correct once the smart contract is deployed to execute.
Note: One solution that blockchain developers follow to correct this is De-facto mutability. Although the code is – in a number of terms – immutable, developers follow the de-facto mutability principle by having segments of code in other contracts, and having the address of which contracts to call stored in the modifiable storage.
2. Cases of Loophole
Unclarity when it comes to ‘implied covenant of good faith and fair dealing’. In the US Law, there is a concept of Good faith, which states that the parties will deal with each other fairly and won’t rob each other off from getting the benefits of the contract.
But, with Smart Contracts, it is difficult to ensure that the terms are met in accordance with what was implied.
Suppose you order an autographed Tennis Ball but what you get is a forged ball. Now, under ordinary circumstances, you would have been able to take the case to the court following the Contract Law, but with Smart Contracts, the possibility is next to nothing.
3.Third Party Elimination
One of the core challenges associated with Smart contracts is ease of elimination of third parties. While elimination of third parties is a paradigm that has been set for Blockchain and Smart Contract, likewise, the concept in no way eliminates them.
Take lawyers for example. While yes, it is true that users will not have to go to them to get the contract made, developers will have to be in contact with lawyers to know the terms on which the smart contract will be based.
In the end, the involvement of third-party entities never goes away, they just take up different roles from what they take in the non-decentralized smart contract.
4. Legal Unclarity
Disputes are the elements that play an inherent role in Smart Contracts in the blockchain ecosystem. While in case of paper contracts, it can come as a result of an ambiguous statement like ‘Sufficient Cause’, in Smart Contract, it can come as soon as the user passes a statement saying that the code is bugged.
To determine which party is right, users will ultimately have to resort to starting a legal procedure – avoiding which was the one reason Smart Contract was ever brought into existence.
There are multiple options when it comes to handling disputes with Smart Contract –
- The one option to solve disputes in Smart Contract is to rely on votes. If there are multiple parties involved in the contract, businesses can call a vote and decide which party is in the right.
- Introduction of arbitrator(s), who will act as a judge in case of dispute.
- Making it necessary to have the signature of both the parties before the contract is closed.
5. Management of Vague Terms & Conditions
Contracts are made up of several implied terms and conditions, which are not all in black and white. While it is fairly easy for a smart contract to deal with the transaction where only a very limited set of parties are involved and the event that they have to perform is fairly direct, if you plan on introducing an event like the one used as an example above, smart contracts fail to be the right mode.
Inability to handle vague tncs are one of the major Smart Contract legal issues, which is staring at immediate rectification if the concept wishes to see mass adoption.
These are some of the issues that have come to the surface now when Smart Contracts are yet to see mass adoption. More are expected to come bubbling up as the concept grows and find a place in integral part of all businesses.
In the end, as far as you, as a business, look at the positive sides of the Smart Contract, you will see a number of reasons to introduce the concept in your business, but when you boil it down, a number of limitations come up, which can majorly be resolved in one way.
[Also Read: How to create Cardano smart contracts?]
How to Overcome the Limitations of Smart Contract
Either you work your way around by ignoring the shortcomings of Smart Contract, assuming that the concept will revolutionize your business or you take the right move which would make your Smart Contract, whether it is an Ethereum Smart Contract of one that is based on any other platform, unhackable.
The Right Move talked about here is Hiring a Team of Blockchain Developers who are well accustomed with the concept, have knowledge of Parallel Programming, Know of the kind of bugs that can come in writing the Smart Contract Code.
Only when you invest in a team of Smart Contract experts, you will be able to get a contract that is ready to be complex.



The Rise of Blockchain in Digital Marketing - Benefits, Use Cases and Challenges
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing digital marketing by transforming strategies through its decentralized and secure framework. It provides marketers with unparalleled transparency in campaign tracking and data management, guaranteeing increased security and privacy for users. As the digital landscape is advancing at a fast pace, blockchain in marketing offers the digital marketers with the means to…

Blockchain Interoperability: The Key to Connect Siloed Blockchain Networks
Blockchain has been a revolutionary response for industries facing the growing pressure of centralized operations’ limitations. By building an ecosystem which runs on zero trust, the technology introduced the world with processes that were incredibly neutral, change-proof, and 100% transparent when compared to their predecessors - traditional computing environment. Having reached a stage where blockchain…







