Information Technology is a vast field with a comprehensive glossary few people have consolidated knowledge of. As a result, we see a discrepancy in many online sources with non-related IT terms being used interchangeably. This often happens while discussing enterprise software applications.
The layman tends to mix up enterprise software development and standard software engineering when one is just a subset of the other.
With that thought, it’s time to cover this still not settled topic around the differences between enterprise software development and standard software development. What makes it all the more important now is that the global enterprise mobility market is poised to be worth $140 billion by 2020.
What Does Enterprise Software Mean?
Breaking down the term would self-define it. An enterprise is a business. Software that is tailored to suit the needs of a business is therefore an enterprise software. While a single software might suffice to process particular tasks, a collection of such software packages is needed to support the day-to-day needs of an organization. This collection formulates an Enterprise System (ES). One popular enterprise software solution is Enterprise data warehouse used by modern enterprises to level up their business data processing.
The scope of work of enterprise software applications depends on the nature of business. But it is safe to say that the tools are more or less similar in principle. Owing to this reason you would see Software-as-a-Service vendors offer essentially the same platform, with the option to add or subtract features according to the business need. An enterprise software developer is often tasked with creating the following enterprise level software, which also act as reasons to invest in enterprise app development:
- Payment Processing Tool
- Business Intelligence
- Human Resource Management
- Automated Billing System
- IT Service Management
- Form Automation
- Project Management
- Business process Management
You would notice they require a particular level of enterprise software management to create and operate. Such enterprise project management platforms are efficiency-driven and result oriented.
Software engineering that is concerned with creating a service-focused solution for an organization is called enterprise software engineering. It is limited to a business process or a network of them.
In tandem with the above-mentioned tools, there are certain characteristics that formulate the base of such solutions as detailed in the following section.
Features of Enterprise Software Applications
Enterprise software developers must stay disciplined while conceptualizing an enterprise software product. With the purpose of the software clear, enterprise software applications must manifest the following characteristics regardless of their form-factor and design for they can be a strategy to improve the ROI of an enterprise app:
Performance
You would either have an in-house IT team working full-time on greasing and oiling your processes or an enterprise application development company in Florida or any part of USA doing the bit for you. Since you will expend resources you might as well do it right. Performance management has to top your agenda. When the software powering your business delivers continuum, it automatically reduces your spending on maintenance services.
Ensuring high uptime reflects in the quality of the product meted out to consumers. At the end of the day, the software is a combination of programmable codes which doesn’t run on its own but needs constant monitoring. The only point of concern being, there should be minimal instances of worry as you deputize the functioning of such software.
Scalability
Users would continue to pour into the system as you reach new highs and expand your business. If contracting your work to a custom software development services company in any part of the world, be it an enterprise application development company in Florida or USA, then keep in mind that the architecture insures you against an ever-expanding user count. There should be advance reporting mechanisms baked into the software so effective steps can be undertaken and code inadequacies worked on timely. The enterprise application development company should make it their mission statement to provide the latest technological upgrades as and when needed to scale applications.
Storage
As the number of users multiply, so would their data. You would reach a tipping point when in-house data warehouses would not be sufficient to bear the load of your growing data demand. Cloud storage systems have emerged as a reliable alternative to such a problem. You would find many alternatives in the market to outsource this crucial IT section be it end-to-end SaaS vendors or enterprise software development services
Your technology partner, should you choose to go that way, should have the capability of storing both structured and unstructured data. As we continue to chart the digital economy, support in managing Big Data would be a big plus.
Security
User data is the 21st-century equivalent of oil due to which it must be stored securely. An endemic software loophole could cause a data leak wreaking havoc and causing immeasurable damage to your brand reputation. At the same time, the means you rely on to protect you from potential rogue actors must not violate applicable regulatory guidelines.
One of the enterprise app development myths is that they are hack friendly and thus cannot be trusted with sensitive data. An enterprise app development company can help you fill security gaps provided your business does not have sufficient in-house digital security experts to bank on. Appinventiv has a comprehensive wing of compliance administrators that suits our partners throughout the Americas and beyond. Be it GDPR or other emerging but not yet legalized instructions on such matters, we have a 360-degree approach to keep your enterprise software apps tact and dandy.
Interoperability
We mentioned earlier that Enterprise Resource Systems (ES) are implemented to run large scale business processes. As part of such an interconnected software package, it is vital that enterprise applications interoperate without giving you a headache. While laying out a strategy for such projects make sure your developers are aware of the future scope of current and emerging technological trends.
If you plan to outsource the development, the software application development company must have a long-term view of the state of apps and the experience to make room for 11th-hour client requests.
Microservices
Coming to the architecture of the software, microservices help mitigate software latency by distributing the workload on to separate functional areas operating in cohesion. You realize the true advantage of microservices when there is a peak in demand. It makes business processes flexible and makes them cope with performance-related issues.
But not all developers have the aptitude to work with microservices and they are more in favour of monolithic architecture in the comparison between monolithic and microservices. If your IT team lacks such support, consider partnering with an enterprise mobile application development company seriously.
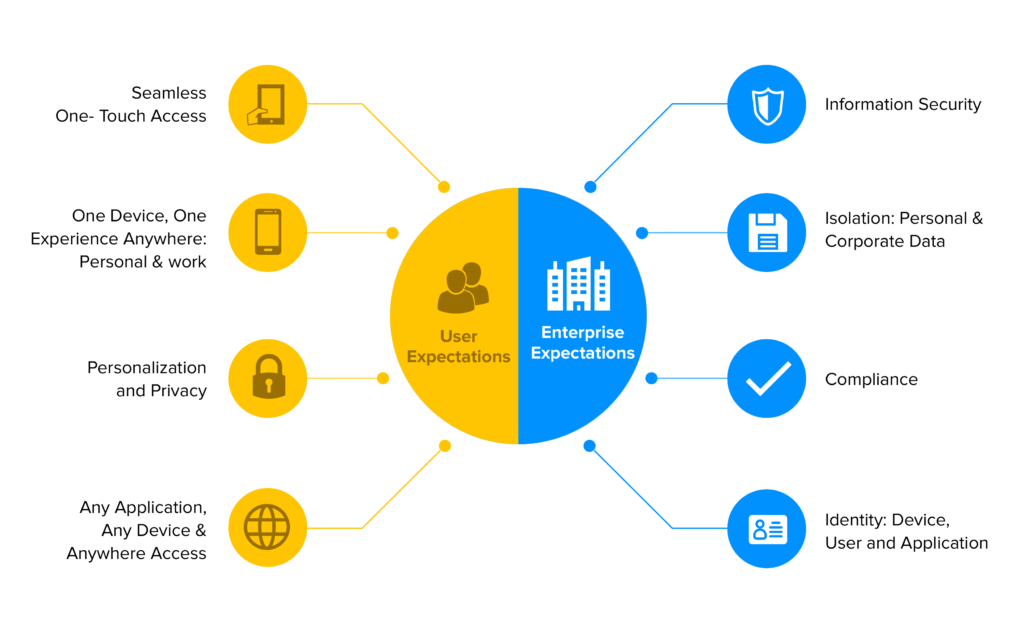
Difference between Enterprise Software and Consumer-End Software
Conventionally, software can be of three types depending upon who the end-user is namely:
Custom – It is designed to meet the requirements of an enterprise, in other words, this is the enterprise software that has been discussed up until now.
Consumer – It is designed with standalone users like yourself in mind. Smartphone applications such as iTunes, Google Maps etc., can be counted amongst consumer software or consumer apps.
Personal – Provided an individual has the requisite knowledge to write code, they can design software for personal use. An example could be an automation software to process calculations.
When people, at large, talk of software, they do so while believing there is no difference between enterprise software and consumer software. You know better now! But to be sure here’s a breakdown of what distinguishes one from the other.
Target Group
The first and foremost differentiator is the target user of each group. While consumer apps are targeted towards the masses, enterprise apps are for businesses. Consumer apps are available on app stores while enterprise applications can be subscribed to on a pay-as-you-go basis from third-party vendors.
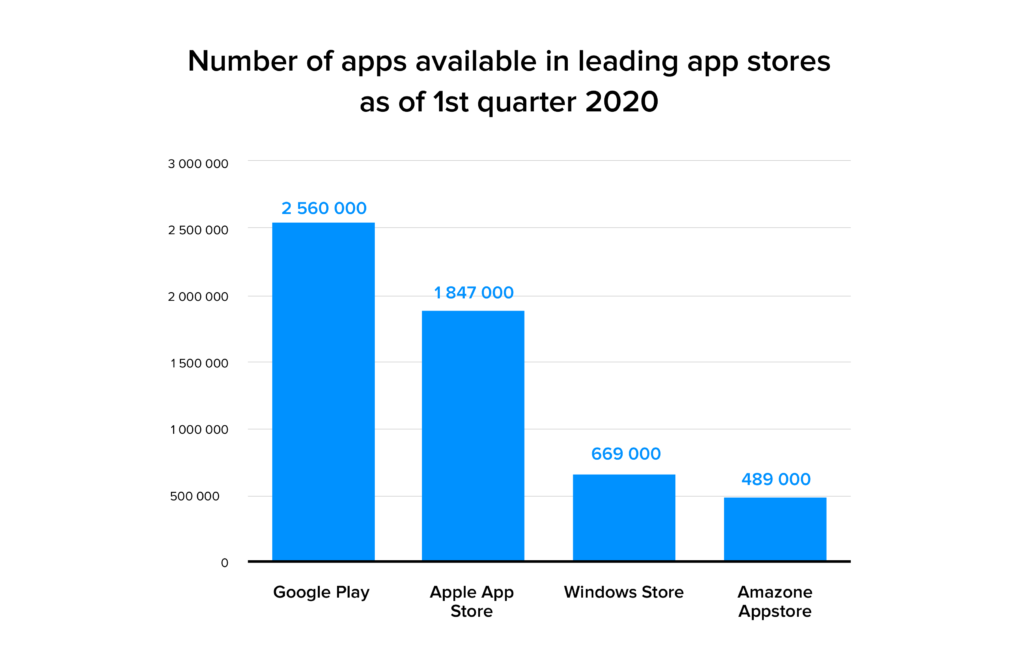
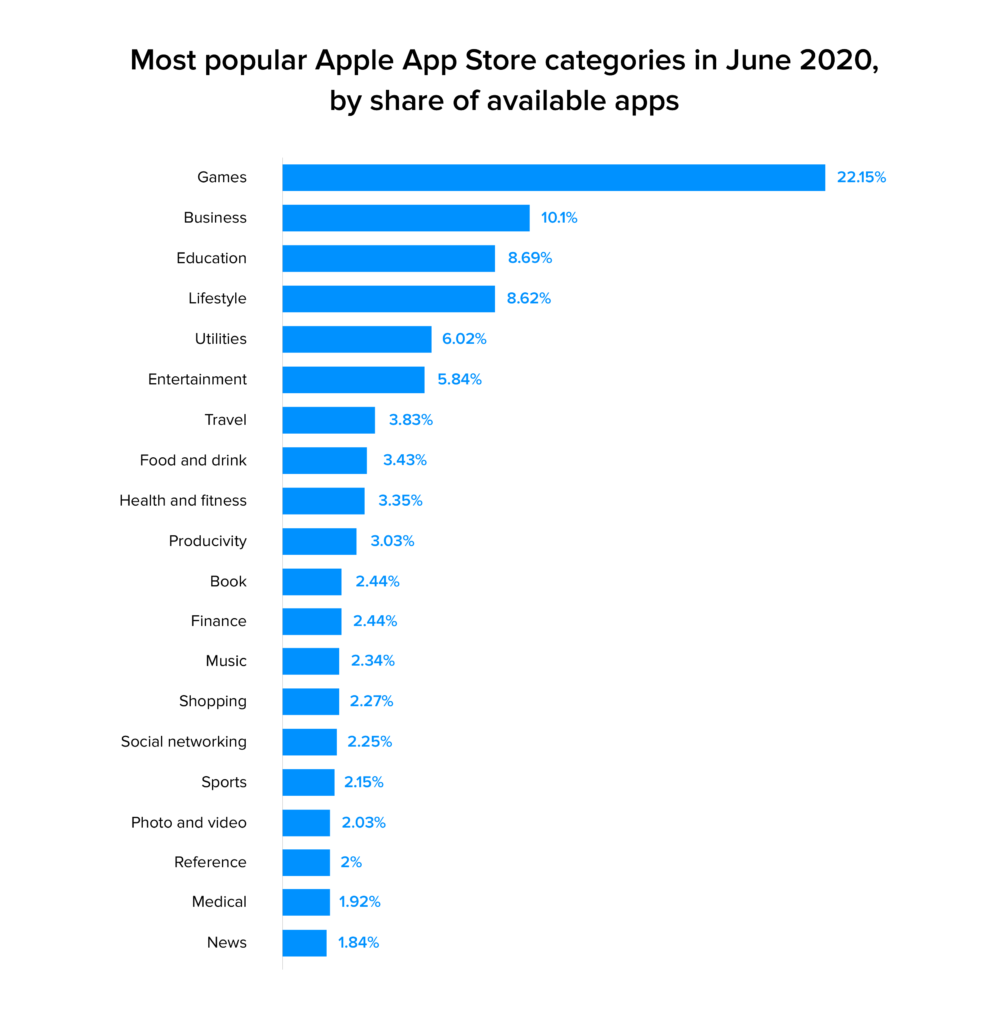
As of the first quarter of 2020, there were more than 2.5 million applications on the Google Play Store alone – reason enough to go with an Android app for enterprise needs. Enterprise apps are much less in number, but it is safe to surmise that they enable the production of consumer apps by helping the business machinery work well. With Appinventiv’s enterprise mobile app development services clients can get both, a consumer app as well as an enterprise app.
Functionalities
Consumer apps are lifestyle driven. Their aim, notwithstanding a few exceptions, is to simplify the choices consumers make in their daily lives. In the digital age, they have come to dictate and monetize every conceivable aspect of human life from leisure to health and more. Each industry defines a category for enterprise mobile app developers to let their creative horses lose and design the next big thing.
Enterprise apps, on the other hand, are driven by optimizations and profitable business outcomes. Irrespective of their function, they are supposed to hammer down on process inefficiencies and smoothen out possible alternatives to save stakeholder time, resources, and capital.
Types
Both the consumer as well as enterprise apps can be further categorized into an open and a closed ecosystem. Open apps are those that the public at large can access. This happens, in terms of smart devices, by downloading the application while the enterprise users have to log into the software with an assigned user-ID and password.
Note that the open and closed supra-category is equally applied to consumers and enterprise apps irrespective of their industrial category. For instance, organizational employees could, at will, log-into an open app such as an internal instant messenger (IM), or learning management system (LMS). A closed app could be a payroll management system.
Design
Design is the central axis of consumer end apps around which UI/UX and the navigational features rotate. An immeasurable amount of thought is channeled into finding that secret sauce of aesthetic elements used to grip user attention. Convenience is the key. App developers are driven by UI/UX trends, the 2020 iteration of which suggests developments such as a passwordless future for app logins.
But there is no such compulsive design thinking to program enterprise apps as they are created to manufacture efficiency. In fact, the more minimalist they are the better as the objective is not to awe the viewer but to resolve queries in minimum time. This is how enterprise software development differs from normal software development.
Facial Recognition in Consumer Apps
Revenue Generation
Consumer apps generate income through two modes. The first is the subscription mode where users pay a monthly fee to avail app services. In app purchases formulate a component of this mode. The second involves indirect monetization where advertisers pay a fee to reach the user base with targeted advertising.
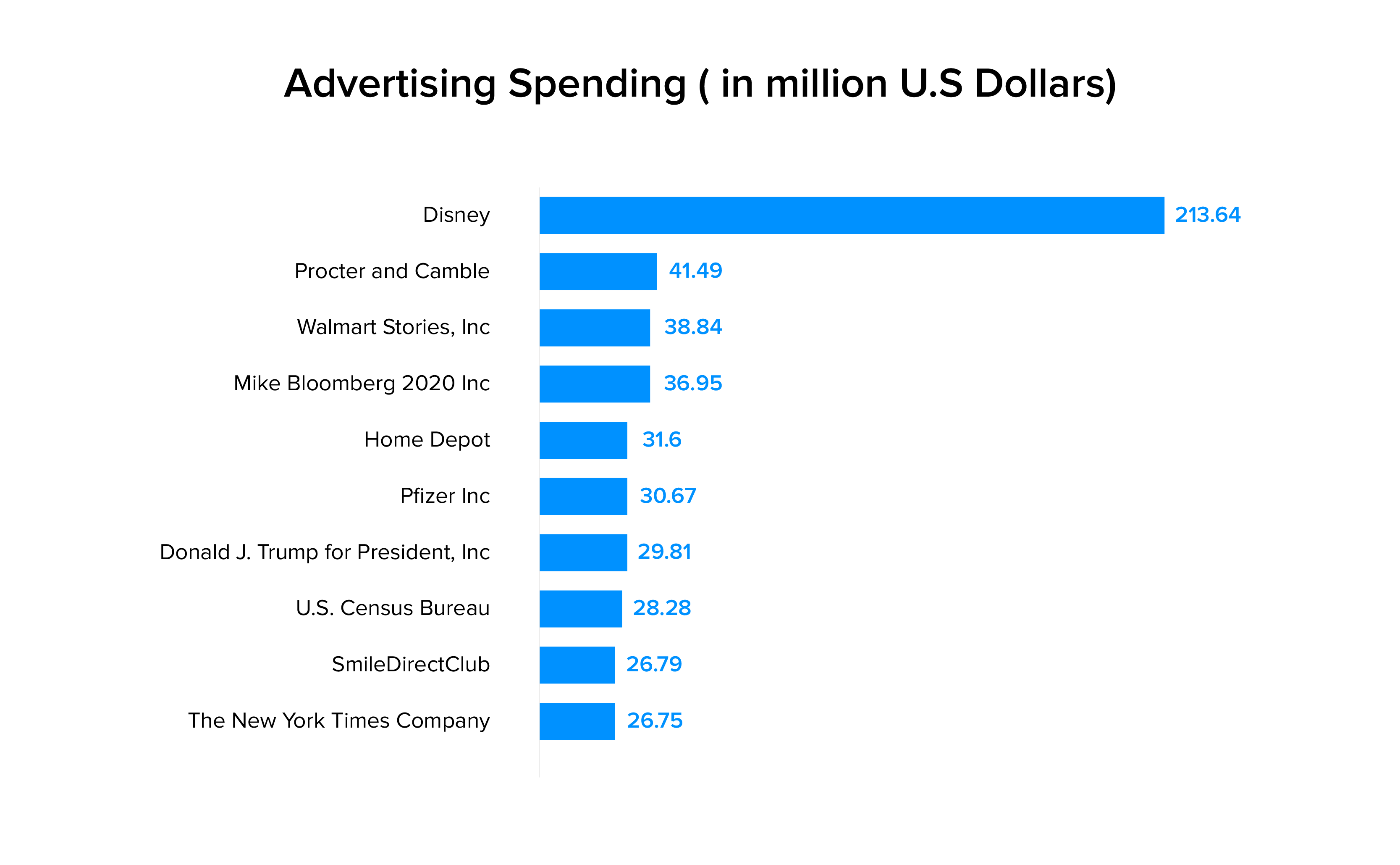
In other words, the apps charge businesses for the structured data that can be used to directly promote a relevant service. Take Facebook for instance. The world’s largest social network has legacy business paying ostentatious sums to reach users with
Disney, spending the maximum in the 1st quarter of 2020 (US $213.64 million).
Enterprise apps also rely on dual modes of income. The first is where B2B clients pay an upfront, lifetime licensing fee for owning the software. The vendor makes all the SLA customizations to the software, following which the latter’s IT team is responsible for the enterprise software management.
The second method is where enterprise software developers have the room to maneuver and maximise profits. Rather than offering the software for a licensing fee, they can negotiate a deal to have a share of the profits. The condition makes perfect sense as the software is designed to optimise efficiencies and deliver results. This is how a standard software vs enterprise software revenue model works.
Concluding Thoughts
Enterprise Software development doesn’t come naturally to all. In cases when it does, vendors limit the span of their services to the macro-economic, B2B sector. But that is not how Appinventiv operates. We offer our partners everything under one roof, be it enterprise application development company in Florida, mobile application development in Asia, or even on-demand development with unprecedented IT solutions that few would conceive. But don’t take our word, see it to believe it.


Enterprise Application Integration - How It Works and Why It Matters to Your Business
In the fast-paced corporate world, CEOs and CTOs are often tasked with managing multiple systems and departments, each playing a crucial role in the success of the company. But what happens when these systems don’t communicate effectively with one another? Imagine your sales team's inability to instantly share data with your inventory management or customer…

Mobile CRM - The Key to Driving Success in the Modern Business Landscape
In a world where business agility translates to success, embracing Mobile CRM can be a game-changer. It provides immediate access to customer data, significantly boosting your responsiveness and operational effectiveness in a competitive market landscape. These systems ensure that relevant customer information is just a tap away, enhancing decision-making, optimizing customer interactions, and significantly boosting…