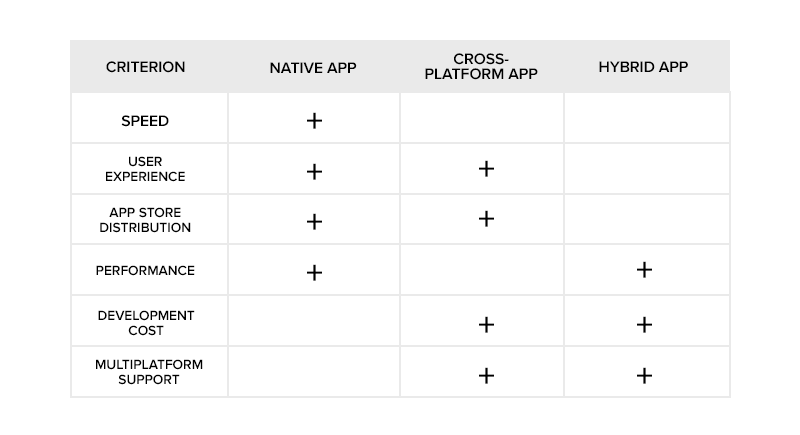
- Types of Mobile Applications
- Native Apps
- Cross-Platform Apps
- Hybrid Apps
- Choosing Your Mobile App Development Tech Stack
- Tech stack for Android mobile development
- Tech stack for iOS mobile development
- Tech stack for cross-platform mobile development
- Technology stack for hybrid apps
- How to Determine Your Tech Stack
- Goal Setting
- Project Estimation
- Deadlines
- Third-Party Integration
- Final Thoughts
The mobile app industry is governed by the interoperating forces of consumer demand and an ever-evolving tech stack for mobile app development. Whereas the former pillar is easy to follow, the latter needs some explaining. A tech stack is a bundle of APIs, programming languages, and tools responsible for the architecture, performance, and development cost of each application. Think of it as a recipe for a tasteful in-app experience. With the competitive forces of iOS and Android at each other’s throats, the mercury hits the ceiling regularly for consumer expectations.
It is critical for product developers to readily integrate AI and machine learning while delivering app functionalities in line with the mobile app tech stack.
But how do you do that? Let us find out!
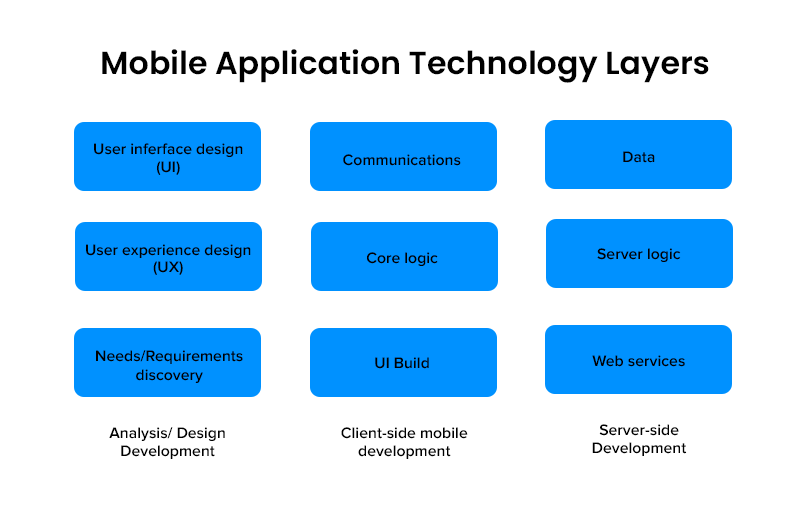
Types of Mobile Applications
Before you jump to hasty conclusions about the technology stack for mobile app development, it is foundational to agree upon the nature of the ‘app’. Chiefly, there are 3 types of mobile apps that are relevant to this discussion, and briefly described below:
Native Apps
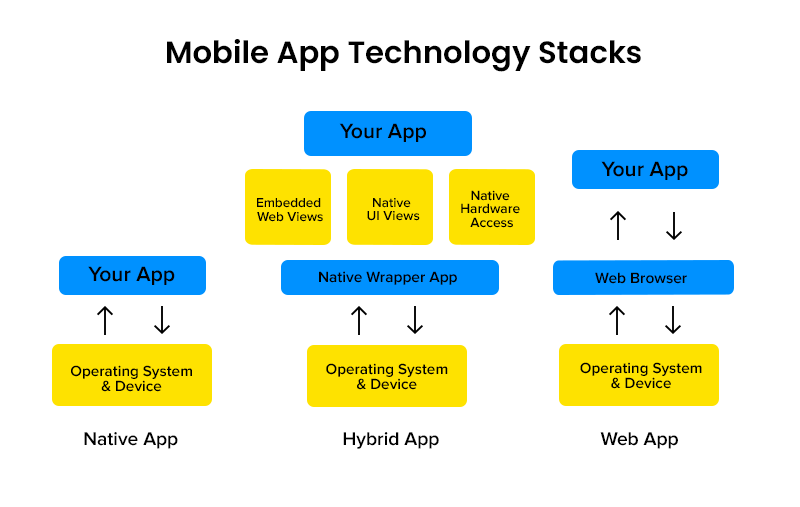
They are indicative of software that is purposed to run on a specific operating system. An app that is natively created for iOS, will not run on Android and vice versa. There is a significant upside in a mobile app technology stack chosen for a native OS. For instance, they can squeeze extra-bits out of built-in mobile features such as the GPS, camera, or movement detector.
Software updates can be transmitted without much to worry about. Although the expense incurred to build native apps can be marginally higher, they make up for it in departments like user preference, and software maximization.
Cross-Platform Apps
It is a dual-purpose software that can run equally well on both android and iOS. The code and the sequence of the software retain their integrity and run perfectly on either OS. They lend a great advantage to cash-crunched teams as creating a unified block of code consumes less time and resources. However, its positives tend to have a loophole in that its quality is subpar to native apps. Process of developing mobile applications with a cross-platform view requires significantly higher service support in the form of version updates.
Hybrid Apps
Hybrid apps take the best form-factor out of native apps and combine them with the advantages of web apps: websites running on the internet and not installed on a device. They are deployed using a native container with the help of a mobile WebView object. When the app is called to action, this object shares the content using a stack for mobile app development built on CSS, HTML5, and JavaScript.
App development services working with an agile mindset report multiple benefits of modeling hybrid apps. For starters, the code is written-once-used-anywhere which reduces development costs and resources.
Choosing Your Mobile App Development Tech Stack
Based on the above descriptions (and a lot of Googling), you will eventually wind up with one of the above categories to design the skeletal details of your app. The following mobile app development technologies of 2021 shall help you solidify the bare essentials of a tech stack.
Tech stack for Android mobile development
Programming Languages used: Java, Kotlin
Java used to be a top choice for Android development until it was overtaken by Kotlin. It is easy to learn, compile and debug. Java code is inherently made to be reused in standard programs. It is platform-independent i.e. it can run on any hardware provided the user has a JVM pre-installed. That said its limitations made Google forsake its use in favor of Kotlin. A major criticism of Java has been its memory consumption which makes it slower-running than other native languages. A reason for this is its memory management practices that use garbage collectors which makes apps slower.
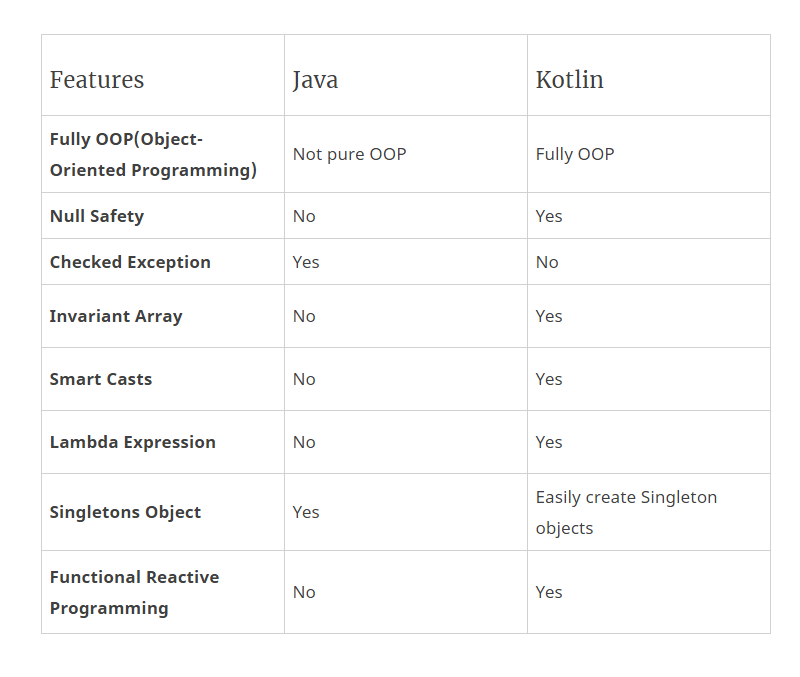
Whereas Java code is distinguishably voluminous, Kotlin is much leaner and to the point. A tech stack for an android app that chooses Java over Kotlin, will face difficulties in innovating micro-interactions and in-app screen transitions. Kotlin is easier to maintain as it supports multiple IDEs including the Android Studio.
Toolkit: Android Studio, Android Developers Tools
The Android Studio is designed to give developers the freedom to create high-performance apps. The entire IDE is based on the premises of faster ideation and iteration. It allows for code interoperability along with cloud integration. With its project structure and grade-based builds, programmers can workaround APKs for multi-device compatibility.
Tech stack for iOS mobile development
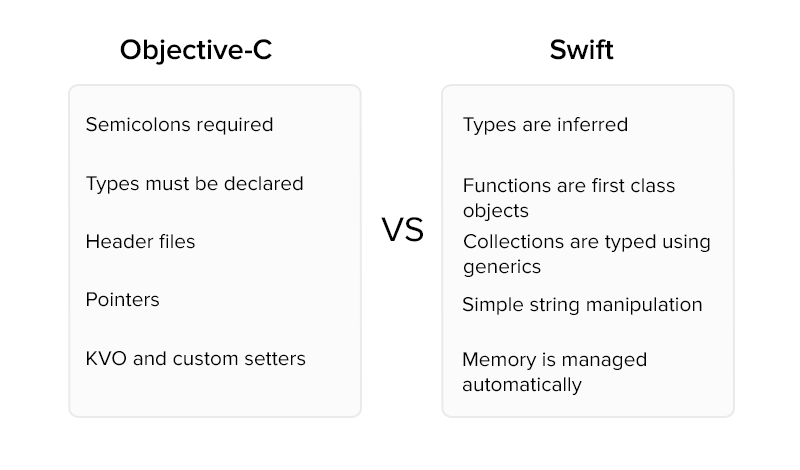
Programming Language – Objective-C, Swift
Objective-C used to be a default choice for iOS development, until Apple, maintaining its competitive edge with Google, introduced Swift. Swift offers a long list of improvements over objective C of which code readability is one, thanks to a concise syntax. This also makes it safe as clean code is easier to debug and maintain. Currently, it falls under the list of top programming languages to consider in 2022 and beyond. This build-up of advantages makes the code executing speed faster than objective-C.
Toolkit – Xcode
Xcode is the IDE for the iOS tech stack, particularly if you decide upon using Swift as the programming language. You can create apps that are compatible with both mobile and desktop. Also, you can download and test apps on beta-versions of stock Apple software such as iOS beta, iPadOS beta, macOS beta, watchOS beta, and tvOS beta. They also offer built-in support for GitHub and internal documentation, and an editor to create aesthetic UIs.
Tech stack for cross-platform mobile development
Cross-Platform app development uses the same code base for multiple devices and therefore cuts short the development time manifold. Here are the most turned-to frameworks for cross-platform app development.
React Native, JavaScript/TypeScript
React Native is a JavaScript-based framework using which you can create apps that have the form-factor and appearance of a native application. Apps built on React native are far more stable than other frameworks. Wide support for 3rd party libraries coupled with the pre-loaded JavaScript packages that it has been designed with, makes it suitable for cross-platform app development. The reusability of code, design options to create stunning user interfaces, and technical support from the community make React Native a safe bet.
Instagram and Skype both use React Native.
TypeScript could also be considered for writing code for React components as error detection is relatively easier to do. It makes the apps safer for end-users.
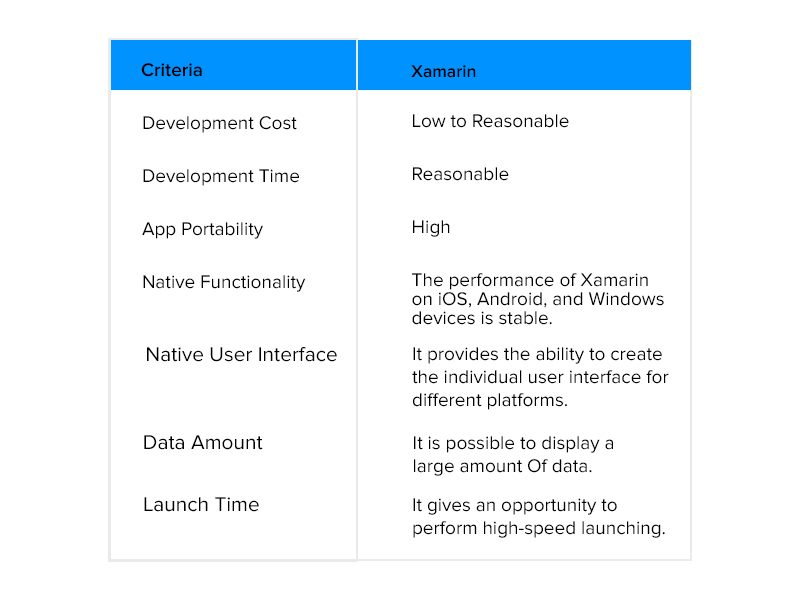
Xamarin, C#
Xamarin is yet another open-source platform using which more code can be shared across cross-platform applications. The Xamarin.Forms UI framework can be leveraged to create single code-base UIs for iOS, Android, Windows apps. It uses C# as its primary computing language. Popular apps built with Xamarin include the likes of Pinterest and Slack.
Technology stack for hybrid apps
Let us now explore what stacks do most mobile app development services deploy for hybrid apps.
Cordova
With Apache Cordova developers get the freedom to use technologies such as HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript. It supports a range of mainstream operating systems such as Ubuntu, iOS, Android, and Windows. With its device installer format you only need to write the source code once, and subsequently pack it for the respective operating systems. Cordova has pre-designed app templates with ready-to-use code bases that mitigate development time for hybrid apps. This open-source platform offers plugins that allow apps to access a device’s hardware functionalities such as the camera, GPS, and file systems.
Ionic
This is an Angular-JS framework that is preferred for modeling Progressive Web Apps (PWAs). Designing high-spec apps for a mobile app development company is easier with its feature-rich library of UI components. Ionic apps are pre-configured to handle cloud workloads integrating freely with AWS, Azure, and Firebase. The IDE – Appflow, is a plug-and-play suite of Mobile DevOps services that automates each app lifecycle phase. Ionic has a worldwide community of 5 million developers, so you can imagine the support in case of technical bottlenecks. Ionic framework is mostly preferred for PWA development.
![]()
How to Determine Your Tech Stack
Being a mobile application development company in the USA we can state with authority that a tech stack cannot be a one size fits all mindset. Each toolset should be rendered as per the project requirement. Go to the drawing board and estimate your resources based on the following factors:
Goal Setting
Map all the requirements that your app ought to pack a punch with. After deciding its nature, native/cross-platform/hybrid lay down the marker for its integral specs and outer architecture.
Project Estimation
“Budget” is the elephant in the room you need to address. Post finalizing the app functionality and forecasting the required expenditures, you can customize the stack as per your needs.
Deadlines
As a frequently awarded mobile application development company, we at Appinventiv keep deadlines close to our heart. Based on which we decide which toolsets to invoke and get the job done in time. We recommend no different to others.
Third-Party Integration
Take this seriously. Concerns over cyber theft continue to halo data exchange between third-party apps. Try and close down any backdoor entries to your app that could leak user information to maleficent actors.
Final Thoughts
The right tech stack could marry your product development efforts with widespread success. The risk of doing it otherwise pounds hard on losers. With a service staff of 600+ qualified personnel, give Appinventiv a chance to push your idea to the next level.



How to Hire an App Developers in Australia?
Australia is rapidly becoming a hub of technological innovation. Businesses across sectors are thriving due to advancements in scalability through digital transformation and cutting-edge solutions. With a strong focus on fostering creativity and growth, the tech landscape has become a driving force behind business success. Among the innovations propelling industries forward, mobile apps have emerged…
How to Hire the Best Mobile App Developer in Dubai, UAE? Key Steps, Costs, and More
The prominence of mobile apps across various industries, including healthcare, eCommerce, and finance has become a global phenomenon, revolutionizing the way businesses operate and interact with their customers. These apps have enabled professionals and users alike to interact seamlessly across distances, breaking down geographical barriers and providing services that were once only available in person.…








