- Importance of Cybersecurity in the Banking Sector
- Understanding the Key Benefits of Cybersecurity in Banking
- Operational Continuity
- Improved Risk Management
- Cost Efficiency
- Enhanced Data Protection
- Enhanced Incident Response
- Increased Customer Trust
- Enabling Digital Innovation
- Key Use Cases of Cybersecurity in the Banking Industry with Real-Life Examples
- Citibank’s Endpoint Protection Strategies
- JP Morgan Chase’s Using AI & ML for Fraud Detection
- Wells Fargo’s Utilization of Multifactor Authentication
- Barclay’s Incident Management Policies
- A Look at the Types of Cyber Security Solutions for Banks
- SRC-TI (Threat Intelligence)
- SRC-AttackGuard
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Cloud Security Solutions
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Cybersecurity Best Practices for Modern Banking
- Implement Strong Authentication Mechanisms
- Regularly Update and Patch Systems
- Conduct Regular Security Audits and Assessments
- Protect Sensitive Data
- Monitor and Respond to Security Incidents
- Secure Network and IT Infrastructure
- Backup and Recovery
- Adhere to Regulatory Compliance
- Manage Vendor and Third-Party Risks
- Educate and Train Employees
- Overcoming Cybersecurity Challenges in Banking - Key Implementation Issues and Effective Solutions
- Complex Regulatory Environment
- Data Protection and Privacy
- Integration of Emerging Technologies
- Legacy Systems and Infrastructure
- Strengthen Your Cyber Defenses with Appinventiv’s Expertise
- FAQs
In today’s hyper-connected world, the financial sector faces an escalating battle against cyber threats that threaten not only operational stability but also its very existence. Traditional banking and FinTech models, once reinforced by legacy systems and manual processes, are now vulnerable to a wave of advanced cyberattacks, making robust and adaptive cybersecurity measures more crucial than ever.
Recent breaches highlight the severity of these threats. In early 2024, major banks suffered a significant ransomware attack, while a leading FinTech firm experienced a substantial data heist. For instance, Evolve Bank and Trust confirmed a cybersecurity incident where customer data was illegally released on the dark web, as reported by Reuters. Additionally, a breach at Infosys McCamish Systems, disclosed in a Forbes report, led to a data compromise impacting over 57,000 Bank of America customers, according to an IMS breach notification letter filed with the Attorney General of Maine.
The rapidly evolving threat landscape demands not only enhanced defenses but also innovative, adaptive strategies to preempt and respond to emerging cyber threats. In response, the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) aims to overhaul the industry by introducing stringent cybersecurity standards. It has now become mandatory for financial institutions to comply with these new regulations from 2025, or face severe penalties and reputational damage.
With the DORA enforcement deadline approaching, banks and other financial institutions are now urgently working to upgrade their cybersecurity frameworks. In this dynamic environment, robust cybersecurity is, thus, not merely a compliance requirement but a cornerstone of operational resilience and the future viability of financial innovation.
In this blog, we will explore the importance of cybersecurity in banking. We’ll examine the various types of cybersecurity solutions for banks, their key benefits, best practices, notable use cases, and the main implementation challenges, along with practical solutions. Let’s dive in.
Also Read: Cybersecurity in FinTech Industry – How to Build a Financial App with Proactive Security Measures?
Importance of Cybersecurity in the Banking Sector
With banks managing substantial amounts of personal and financial information on an everyday basis, it always keeps them as prime targets for cyberattacks. In such a scenario, cyber regulations are seen as a key strategy for mitigating risks associated with cyber attacks. According to a 2024 World Economic Forum survey, 60.4% of FinTech organizations believe that stringent cyber and privacy regulations play a significant role in reducing cyber threats.
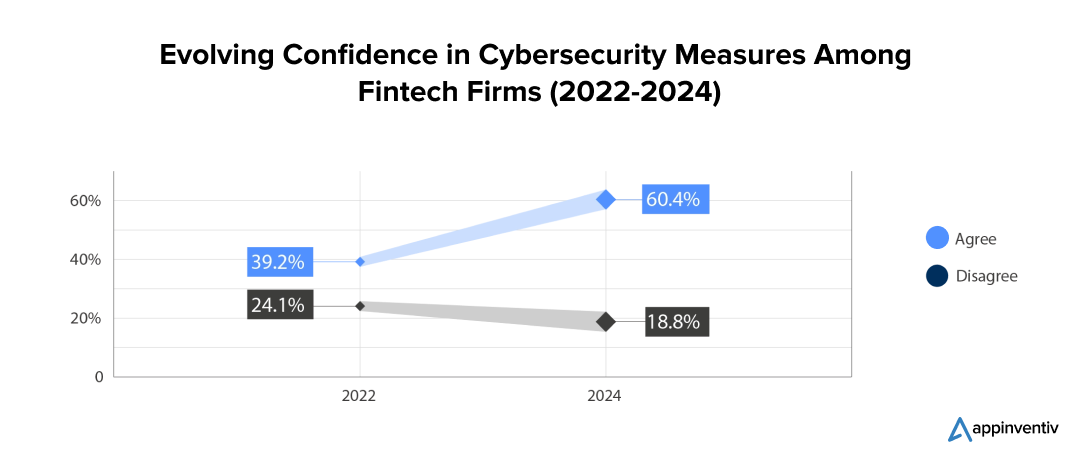
By implementing strong cybersecurity measures, banks can prevent unauthorized access and theft, which helps keep client information safe and prevents identity fraud. Adhering to strict regulations also requires solid security practices to avoid legal issues.
Additionally, cybersecurity is crucial for keeping operations running smoothly and preventing disruptions that could affect transactions. As banks adopt new technologies and digital tools, staying ahead of evolving threats becomes even more important to ensure both security and trust in financial services.
Understanding the Key Benefits of Cybersecurity in Banking
Effective cybersecurity in the banking sector not only protects against breaches but also enhances operational stability and builds customer trust. Let’s explore some of the key benefits.
Operational Continuity
Cybersecurity is essential for ensuring operational continuity and preventing disruptions in banking services. Robust security measures help protect against cyberattacks that could otherwise lead to system outages, data loss, or service interruptions.
By implementing comprehensive defenses and having well-defined incident response plans, banks can ensure that critical operations such as transaction processing and account management remain unaffected by security incidents. This continuity is vital for sustaining customer satisfaction and ensuring that financial services are consistently available and reliable.
Improved Risk Management
A comprehensive cybersecurity framework enhances a bank’s ability to manage and mitigate risks effectively. Banks can identify and address potential security weaknesses through regular threat assessments, vulnerability scans, and risk evaluations.
This approach to risk management helps reduce overall exposure to threats and strengthens the bank’s defenses against emerging risks. By continuously evaluating and improving security measures, banks can create a more resilient security posture capable of adapting to new challenges and maintaining robust protection.
Cost Efficiency
Investing in cyber security for banks can lead to higher cost savings in the long run by reducing the frequency and severity of security incidents. By preventing breaches and mitigating the financial impact of cyberattacks, banks can avoid the high costs associated with data loss, legal proceedings, and recovery efforts.
Prioritizing cybersecurity investments based on risk assessments allows banks to allocate resources more effectively and manage expenditures efficiently. This cost efficiency supports the bank’s financial health and enhances overall operational effectiveness, contributing to sustainable business performance.
Enhanced Data Protection
Implementing strong cybersecurity measures is crucial for safeguarding sensitive customer data, including personal identification, financial transactions, and account details. By employing advanced encryption techniques, secure access controls, and routine security updates, banks can ensure that their data remains shielded and confidential from unauthorized access.
This comprehensive protection helps mitigate the risk of data breaches and theft, preserving the integrity of information and boosting customer trust. It also helps avoid the significant financial and reputational damage that could result from unauthorized data exposure.
Enhanced Incident Response
A strong cybersecurity framework includes a well-defined incident response plan that allows banks to quickly detect, contain, and recover from security breaches. Having established procedures and appropriate tools in place enables banks to minimize the impact of cyberattacks and resume normal operations more efficiently.
This rapid response capability is essential for limiting damage, reducing downtime, and preventing further breaches. A robust incident response plan supports both immediate damage control and long-term recovery efforts, ensuring a swift return to operational stability.
Increased Customer Trust
Effective cybersecurity in the banking industry builds and maintains customer trust by ensuring that personal and financial information is kept safe. When customers are assured that their data is protected from cyber threats, they are more likely to use online and mobile banking services with confidence.
This enhanced trust is crucial for fostering long-term customer relationships and encouraging brand loyalty. In a digital age where data breaches are increasingly common, maintaining robust security measures helps banks strengthen their reputation and retain existing clients while attracting new ones.
Enabling Digital Innovation
Robust cybersecurity provides a secure foundation for banks to adopt and implement new technologies and digital solutions. As banks explore technological innovations like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and blockchain, they must protect their business processes and operations from cyber threats.
Effective security measures allow banks to pursue technological advancements with confidence, knowing that their new systems and applications are secure. This secure environment enables the safe implementation of innovative services and products, enhancing the bank’s ability to stay competitive and meet the gradually changing customer demands.
Key Use Cases of Cybersecurity in the Banking Industry with Real-Life Examples
FinTech giants have leveraged advanced cybersecurity solutions to shield their banking institutions from malicious threats effectively. Let’s explore some top use cases of cybersecurity in banking, which demonstrate how targeted measures tackle specific challenges and safeguard transactions, data, and overall system integrity.
Citibank’s Endpoint Protection Strategies
Banks implement endpoint protection strategies to secure devices such as computers and mobile phones from malware and various cyber threats. This ensures that every endpoint within the organization is protected, preventing them from becoming potential entry points for cybercriminals.
Citibank utilizes an extensive endpoint protection system to secure user information during online banking. Key elements of their strategy include 128-bit encryption for safeguarding transaction data, additional authentication like ‘One-time Authorization Codes’ or ‘Passwords’ for sensitive transactions, and displaying the date and time of the last login to help users identify unauthorized access.
They also use Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates to validate the site’s security, maintain multiple firewalls to shield their servers, and implement session timeouts that require re-authentication after periods of inactivity, all contributing to a thorough security approach.
JP Morgan Chase’s Using AI & ML for Fraud Detection
In the context of fraud detection and prevention, AI and ML algorithms are employed to scrutinize extensive transaction data to uncover patterns and anomalies that might indicate fraudulent activities. These advanced systems are designed to analyze data in real-time, allowing for the immediate identification and interception of suspicious transactions, which helps in mitigating financial losses.
For example, JPMorgan Chase leverages sophisticated AI and ML models to monitor transaction patterns as they occur. The algorithms assess various factors, including transaction frequency, geographic location, transaction amounts, and user behavior, to identify deviations from normal patterns that could signal fraud.
This proactive approach enables the bank to detect and halt potentially fraudulent transactions before they are completed, thereby minimizing financial risks and bolstering the security of customer accounts.
Wells Fargo’s Utilization of Multifactor Authentication
Banks employ multi factor authentication (MFA) and robust access control protocols to guarantee that only permitted individuals can access sensitive systems and data. These practices are vital for blocking unauthorized access and minimizing the risk of credential theft.
Wells Fargo utilizes multifactor authentication for both customers and employees to enhance security. For online banking, customers are required to provide an additional verification step, such as a code sent through text message, in addition to their password.
To further strengthen account protection, customers can activate Wells Fargo’s 2FA feature, known as 2-Step Verification at Sign-On. This additional security layer ensures that only authorized users can gain access to their accounts, thereby significantly reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access.
Barclay’s Incident Management Policies
Banks establish dedicated incident response teams and protocols to address and manage cybersecurity incidents promptly. This involves detecting breaches, containing threats, and recovering from attacks, ensuring that any disruptions are minimized and future risks are mitigated.
Barclays has a specialized cybersecurity incident response team tasked with managing security breaches and cyber threats. This team is responsible for swiftly identifying the source of attacks, containing the damage, and restoring normal operations. Additionally, Barclays’ team conducts thorough post-incident analyses to understand the attack’s impact, refine security measures, and implement strategies for preventing similar incidents in the future.
A Look at the Types of Cyber Security Solutions for Banks
Cybersecurity solutions in banking are specifically crafted to defend against various threats and vulnerabilities. Let’s examine some key solutions and how each contributes to a robust security strategy for financial institutions.
SRC-TI (Threat Intelligence)
SRC-TI, or Security Research Center – Threat Intelligence, is dedicated to gathering and analyzing data on emerging cyber threats from various sources, including dark web monitoring, security forums, and threat databases. This solution plays a crucial role in strengthening cyber security in banking by providing valuable insights that help banks anticipate and prepare for potential attacks.
By integrating threat data into its security strategy, SRC-TI enhances protection and enables proactive defense measures. This actionable intelligence allows banks to quickly adapt to new threats and reduce their window of vulnerability, ensuring a more robust cybersecurity posture.
SRC-AttackGuard
SRC-AttackGuard is a specialized tool designed to defend against a wide range of cyberattacks, including ransomware, phishing, and advanced persistent threats. It includes features for attack prevention, real-time monitoring, and incident response, providing a comprehensive approach to security.
By offering advanced defenses and mitigation strategies, SRC-AttackGuard helps banks protect their systems from various cyber threats.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze security data from various sources to provide real-time visibility into the bank’s security posture. SIEM solutions help detect, respond to, and investigate potential threats by correlating data and generating alerts for suspicious activities.
Cloud Security Solutions
As banks increasingly use cloud services, implementing cloud security solutions becomes crucial. These solutions include cloud access security brokers (CASBs), cloud security posture management (CSPM), and encryption tools designed to safeguard data and applications in cloud environments.
Effective cloud security solutions not only safeguard against unauthorized access and data breaches but also ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. By providing real-time monitoring and automated threat detection, these tools help banks maintain the integrity and confidentiality of their cloud-based assets, thereby enhancing overall cybersecurity in the banking sector.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions monitor and control the movement of sensitive data within and outside the organization. DLP tools enforce policies to prevent unauthorized data transfers and protect against data breaches. By restricting access and sharing of critical information, these tools help safeguard valuable data.
Additionally, DLP solutions provide detailed reporting and alerts on potential data leaks, allowing banks to quickly address and mitigate risks associated with data exposure.
Cybersecurity Best Practices for Modern Banking
Adhering to the cybersecurity best practices is essential for protecting sensitive financial data and maintaining system integrity. By implementing these critical cybersecurity in banking best practices, banks can effectively guard against emerging threats and ensure robust security across their operations. Let’s delve into the same.
Implement Strong Authentication Mechanisms
Ensuring robust authentication is key to protecting banking systems. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security. This step requires the users to fill multiple verification forms before granting access to critical systems and sensitive information.

In addition, strict password policies should be enforced, and password managers should be encouraged to help users create and maintain strong, unique passwords. This combination of measures makes unauthorized access significantly more challenging and enhances overall system security.
Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Keeping systems up-to-date is essential for defending against known vulnerabilities and is one of the most important practices of cyber security in the banking sector. Apply security patches to all software, operating systems, and applications as soon as they become available to address any weaknesses.
Automate the update process whenever possible to ensure timely patching and reduce the risk of exposure to security threats. Consistent updates help maintain the integrity of your systems and protect against evolving cyber threats.
Conduct Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Regular security assessments are of utmost importance for identifying and addressing potential weaknesses in your systems. Perform vulnerability scans to detect any security gaps and follow up with penetration testing to evaluate the effectiveness of your current security controls.
These practices of cybersecurity in the banking industry offer valuable insights into vulnerabilities and help you strengthen your security posture by addressing any identified risks, ensuring that your defenses remain effective.
Protect Sensitive Data
Data protection is a cornerstone of cybersecurity in banking. Implement strong encryption methods to secure sensitive information both during transmission and while it is stored. Enforce strict access controls to affirm that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data, using role-based access controls (RBAC) to enforce these restrictions.
Regularly review and update these security measures to adapt to new threats and ensure ongoing compliance with data security regulations.
Monitor and Respond to Security Incidents
Effective monitoring and response strategies are crucial for managing security breaches. Utilize SIEM systems to collect, analyze, and correlate security event data in real-time for prompt threat detection.
Develop a detailed incident response plan that clearly outlines procedures for managing breaches and conduct regular drills to ensure staff are well-prepared. Establish clear communication protocols to inform stakeholders about incidents and the actions being taken to address them.
Secure Network and IT Infrastructure
Securing network and IT infrastructure is critical for protecting against unauthorized access and monitoring suspicious activity. Set up firewalls to prevent unauthorized access and use Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) to monitor network traffic for potential threats.
Utilize network segmentation to separate critical systems, minimizing the impact of any security breaches. Regularly assess and update your network security practices to stay proactive against cyber threats and improve overall protection.
Backup and Recovery
Implementing effective backup and recovery practices is essential for data protection and business continuity when it comes to eliminating cyber security threats in the banking sector. Regularly back up critical data and systems to secure locations and ensure that backups are protected from unauthorized access.
Test your recovery procedures frequently to verify that data can be seamlessly restored in the event of data loss or corruption. Utilize redundant backup solutions to further safeguard against data loss and minimize operational disruptions during emergencies.
Adhere to Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to regulatory compliance is crucial for maintaining legal and operational standards. Stay informed about relevant cybersecurity and data regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, PIPEDA, SOC 2, GLBA, IEEE, and PCI-DSS, and ensure that your cybersecurity practices meet these requirements.
Conduct regular compliance audits to verify that your practices align with regulations, avoid potential penalties, and demonstrate your commitment to maintaining high-security standards. This proactive approach helps mitigate legal risks and reinforces trust in your organization’s data management practices.
Manage Vendor and Third-Party Risks
Managing and mitigating the risks associated with third parties is vital for overall cyber security in the banking sector. Evaluate the security practices of all third-party vendors before establishing relationships to ensure they meet your cybersecurity standards.
Include specific security requirements in contracts and conduct regular assessments to verify ongoing compliance. This approach helps mitigate risks external parties introduce and ensures that their security measures align with your own standards.
Educate and Train Employees
Training and educating employees is essential for preventing cyber security threats in the banking sector. Offer ongoing training to empower employees to spot and steer clear of common threats.
Encourage a strong security culture where team members understand their responsibility in protecting company assets, stay alert, and practice good cybersecurity habits. This proactive approach helps minimize human error and strengthens the overall defense against cyber threats.
Overcoming Cybersecurity Challenges in Banking – Key Implementation Issues and Effective Solutions
The implementation of cybersecurity in banking comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding and tackling these challenges with strategic solutions can enhance security measures and protect financial assets. Let’s delve into those.

Complex Regulatory Environment
Complex regulatory environment is one of the key challenges in implementing cybersecurity in banking. Banks must navigate a complex and diverse set of regulations across various jurisdictions, which can be difficult to manage and comply with, potentially leading to compliance gaps and administrative burdens.
Solution: Develop a robust compliance software that seamlessly integrates regulatory requirements into the overall cybersecurity strategy. Regular staff training on current regulations and best practices ensures ongoing compliance and minimizes the risk of violations.
Data Protection and Privacy
Managing huge amounts of sensitive customer data is critical for banks, especially in ensuring protection while complying with privacy regulations. This complex task demands significant resources, particularly as data volumes grow.
Solution: Implement strong encryption techniques to safeguard data both while stored and during transmission, ensuring protection against unauthorized access. Employ data masking and tokenization techniques to safeguard sensitive information.
Integration of Emerging Technologies
The integration of advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain introduces new vulnerabilities and complexities that require specialized knowledge and proactive measures.
Solution: Conduct comprehensive security evaluations and risk assessments before deploying new technologies. Follow security standards tailored to each emerging technology.
Legacy Systems and Infrastructure
Many banks still depend on outdated legacy systems that often lack compatibility with modern security measures. These systems are more vulnerable to cyberattacks and can be challenging and costly to secure.
Solution: Gradually update legacy systems by integrating them with newer, more secure technologies. Implement a phased approach to infrastructure upgrades to ensure they align with advanced security protocols. Prioritize the modernization of the most vulnerable systems first to mitigate overall risk.
Strengthen Your Cyber Defenses with Appinventiv’s Expertise
The future of cybersecurity in banking will increasingly emphasize adaptive security frameworks and real-time threat intelligence to tackle new challenges. As banks adopt more integrated digital solutions, safeguarding interconnected systems and data becomes crucial. Innovations such as quantum cryptography can redefine data protection, and decentralized identity technologies could enhance authentication processes.
Appinventiv, as a globally trusted cybersecurity solution provider is leading the way in these advancements with its state-of-the-art solutions. Through its successful projects like Mudra and EdFundo, Appinventiv proves its expertise in delivering secure and advanced solutions for FinTech companies.
Partnering with Appinventiv allows banks and other FinTech organizations to harness expert knowledge and advanced technologies to build resilient security systems. Our journey in cybersecurity as a service has led to significant milestones in risk management and compliance. By adhering to the highest standards and achieving industry certifications, we demonstrate our commitment to protecting your digital assets with unparalleled expertise and achievements.
Connect with our experts today to ensure robust defense against evolving threats and facilitate digital transformation in the financial industry.
FAQs
Q. Why is cybersecurity essential in banking?
A. Cybersecurity is vital in banking to safeguard sensitive financial information and ensure the security of transactions. It protects against unauthorized access, data breaches, and fraud, leading to substantial financial losses and damaging a bank’s reputation. Effective cybersecurity measures are essential for meeting regulatory standards and preserving customer trust by defending against evolving cyber threats. This helps maintain operational stability and ensures the confidentiality and integrity of banking activities.
Q. How to implement cybersecurity in the banking sector?
A. The implementation of cybersecurity in banking requires following a few crucial steps:
- Assessment and Planning: Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential threats and set clear cybersecurity objectives that align with your business and regulatory requirements.
- Risk Management and Asset Protection: Inventory your critical assets and implement security measures like encryption and firewalls, along with multi-factor authentication for secure access.
- Threat Detection and Prevention: Utilize tools such as antivirus software and intrusion detection systems for ongoing threat monitoring, ensuring all systems are regularly updated.
- Incident Response and Recovery: Develop a detailed incident response plan and regularly train staff on procedures for managing breaches and communicating with stakeholders.
- Data Protection and Privacy: Encrypt sensitive information and establish regular backup protocols, ensuring compliance with data protection laws and strong privacy practices.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Offer ongoing training to empower employees to recognize cybersecurity threats and cultivate a culture of security within the organization.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and refine cybersecurity policies, staying updated on new risks and emerging threats to enhance your overall security posture.
Q. What are some of the top cybersecurity compliances?
A. Here are some of the top cybersecurity compliances that banking and other financial organizations should adhere to:
- GDPR: Mandates data protection and privacy for individuals in the European Union.
- CCPA: Grants privacy rights and consumer protections for California residents.
- PIPEDA: Regulates data privacy and protection for individuals in Canada.
- SOC 2: Outlines criteria for managing data to protect organizational privacy and interests.
- PCI DSS: Sets security standards for handling payment card information.
- GLBA: Requires financial institutions to protect personal information and disclose privacy practices.
- IEEE: Establishes standards for secure data transmission and network security.














